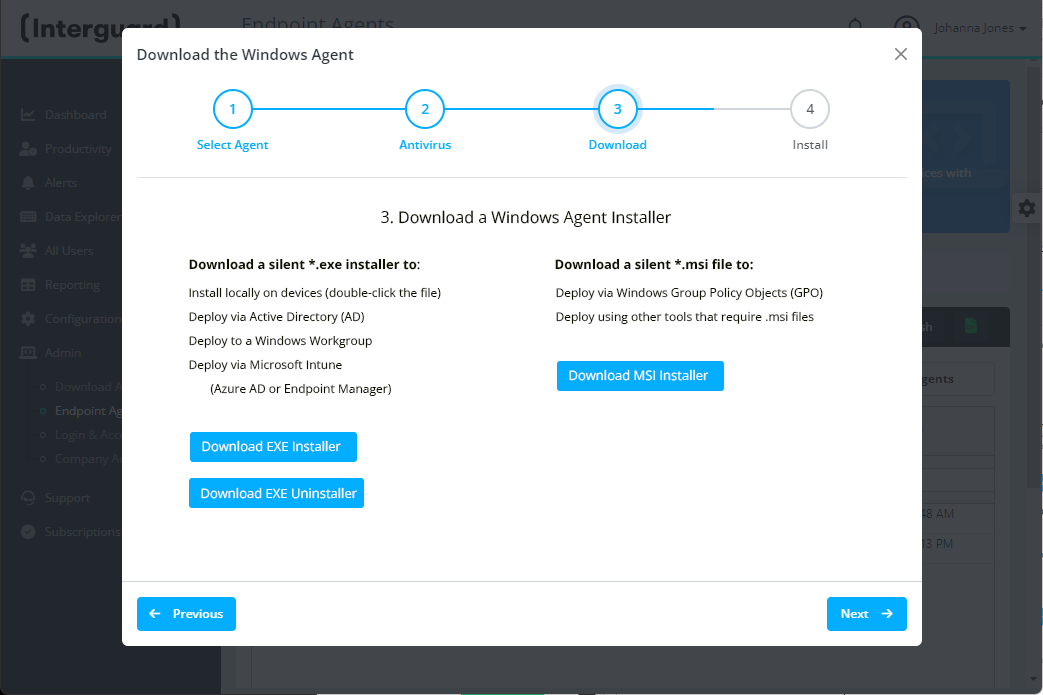
Using the MSI Installer
The Add Agents wizard offers two Windows Installers: an .exe and an .msi file. Both installers are "silent," requiring no interaction once launched. Download one or both installers from Admin | Download Agents. Once you press Generate on the step 3 of the wizard, you can choose to Download one or both files. The best installer to use depends on how you intend to deploy the file to endpoint devices.
NOTE: The installer file may be blocked by local Windows Security. Take steps to unblock the file you haved downloaded before deploying it to endpoints. See Windows Installation: Unblock the downloaded installer file.
Silent EXE Installer
When executed, the .exe file installs the recorder agent silently and registers automatically with the Interguard server. No additional switches are required. Use the .exe file to deploy:
- Locally at an endpoint device (double-click the file)
- Using our NetDeploy tool
- Using PsExec
- Using ConnectWise Manage
- Using Microsoft Intune (once the .exe is converted to .intunewin)
- Using another tool that accepts an EXE install file
The EXE Installer includes an Uninstaller (the MSI Installer does not).
Silent MSI Installer
The MSI installer is our.exe silent installer in an Microsoft Windows Installer (MSI) wrapper. Use the .msi file to deploy:
- Locally at an endpoint device (double-click the file)
- Using Group Policy Object (GPO requires MSI)
- Using another tool requiring MSI for network-based deployments
Learn about Group Policy Object (GPO) deployment here:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/troubleshoot/windows-server/group-policy/use-group-policy-to-install-software
You can deploy both the EXE and MSI Installers silently across a network. However, we recommend using the EXE Installer when possible because at this time the MSI leaves an entry, a generic “Security Update," in Windows Add/Remove Programs.
NOTE: All agents are upgraded using an automatic process that does not require redeployment.
Updated: 01/23/2023